AUSTRIA
![]()
SUMMARY OF POLICIES AND LEGISLATION FOR FOOD WASTE PREVENTION AND REDUCTION
Austria does not have a national plan specifically addressing food waste prevention. However a Federal Waste Management Plan (2011) is currently in place. The aforementioned Plan summarizes the current status of waste management including the amounts of different waste streams and their treatment paths, number and condition of treatment facilities and perspectives for the next period.
Although a specific national target is not set, the overarching goal of the Austrian food waste policy-mix is to reduce the amount of food waste which is produced on a whole and to recover it, thanks to the introduction of a separate collection system. As a matter of fact the Ordinance on separate collection of biowaste is the main law concerning food waste. The ordinance requires biogenous waste to be collected separately unless it is recovered by the household or generator.
Figure 1. Austria’s Policy Mix at December 2014
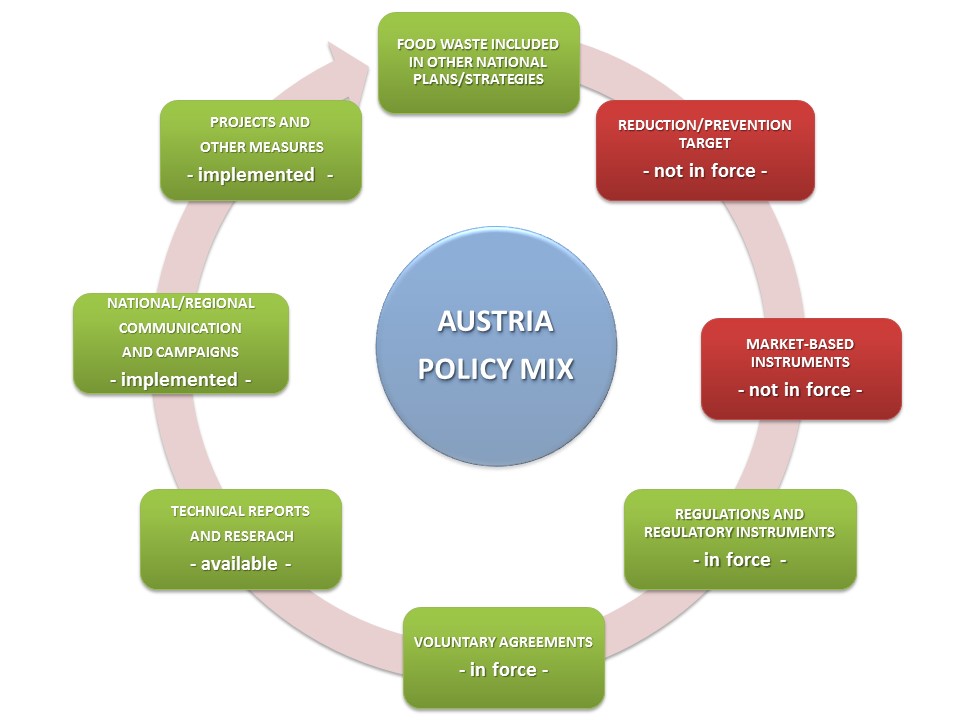
Overall food waste policies mainly refer to: pre-treatment of household waste, separate collection of biogenous waste that is particularly suited for recovery, use of old bread for animal feed, biogas plants which use materials other than agricultural substrates to obtain a reduced tariff by 30%, and food labelling (food with an expired ‘best before’ date for food products to be put on the marketevidently marked with ‘use by’ (‘zu verbrauchen bis’) labels to show that should not be used after expiry as it could put consumer’s health at risk.
The Ordinance on animal feed (2010) includes provisions for implementing the Futtermittelgesetz (Law on animal feed). This ordinance serves as the legal basis for the use of waste bread for animal feed (as one of many regulations).
A voluntary agreement launched by the Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management is in place with the aim to promote the exchange of experiences and the development of solutions throughout the food supply chain.
Best practice dissemination and knowledge exchange through several awarness caimpaigns promoted at the national and regional level are a main focus. For example, campaigns can touch on a variety of topics and mix of tools including discussions and plenary presentations, flash mobs, organic food events, movies, exhibitions, cooking workshops, symposia and lectures on food waste. Since 2011 the Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management has started an action to coordinate the increasing number of initiatives on food waste and to offer to the different stakeholders the opportunity to use a unique recognizable logo.
Altough there are no specific educational programmes on food waste formally included in school programmes, a number of trainings and ecucational initiatives are adressed to children and youth.
Even if Austria has no specific laws on food donations, in Vienna the Neighbourhood project towards surplus food transfer (Vienna) has established a local network for surplus food transfer. Target groups are schools and youth centres on the one side and small farmers and companies on the other side. Furthermore, Austria has a food-sharing online platform that was launched in cooperation with Foodsharing.de, the Ministry and the Viennese Food Bank (Wiener Tafel).
Considering that Austria is landlocked and does not have a deep sea fishing industry nor a large fresh water fishing industry, there is little attention on food waste related to fish products.
Since 2004 landfilling of untreated organic waste is banned according to Austrian Landfill ordinance, implementing a limiting value for total organic content of 5 % dry matter.
Download here the full country report and send us your comments.
REFERENCES
A) AUSTRIA’S NATIONAL PLAN/STRATEGY ON FOOD WASTE REDUCTION
Federal Waste Management Plan 2011
Available from: https://www.bundesabfallwirtschaftplan.at
B) MARKET-BASED INSTRUMENTS
None
C) REGULATORY INSTRUMENTS/REGULATIONS TRADING SCHEMES
StF: RGBl. Nr. 177/1909 (letzte Änderung: BGBl. I Nr. 80/2013) Gesetz vom 6. August 1909, betreffend die Abwehr und Tilgung von Tierseuchen (TierseuchenGesetz - Epizooticdiseases law). https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10010172
StF: BGBl. Nr. 68/1992, idF: BGBl. Nr. 456/1994 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Umwelt, Jugend und Familie über die getrennte biogener Abfälle (Ordinance on separate collection of biowaste). https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10010685
StF: BGBl. Nr. 72/1993 zuletzt geändert durch BGBl. II Nr. 165/2008L Verordnung des Bundesministers für Gesundheit, Sport und Konsumentenschutz über die Kennzeichnung von verpackten Lebensmitteln (Lebensmittelkennzeichnungsverordnung 1993 - LMKV) (Ordinance of food labeling).
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10010723
StF: BGBl. Nr. 186/1996 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Land- und Forstwirtschaft über die allgemeine Begrenzung von Abwasseremissionen in Fließgewässer und öffentliche Kanalisationen (AAEV) (General ordinance on sewage water emissions).
Available from: https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10010977
StF: BGBl. II Nr. 39/2008 zuletzt geändert durch BGBl. II Nr. 104/2014 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft über Deponien (Deponieverordnung) (Austrian Landfill ordinance).
Available from: www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20005653
StF: BGBl. I Nr. 139/1999, letzte Änderung BGBl. I Nr. 189/2013 Bundesgesetz über die Herstellung, das Inverkehrbringen und die Verwendung von Futtermitteln, Vormischungen und Zusatzstoffen (Futtermittelgesetz 1999 - FMG 1999) (Law on animal feed).
Available from: https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10011183
StF: LGBl Nr 35/1999, letzte Änderung LGBl Nr 45/2013 Gesetz vom 10. Dezember 1998 über die Vermeidung, Erfassung undBehandlung von Abfällen (Salzburger Abfallwirtschaftsgesetz 1998 - S.AWG Salzburg) (Waste Management Law).
Available from: https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=LrSbg&Gesetzesnummer=10001126
StF: BGBl. II Nr. 292/2001 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft über Qualitätsanforderungen an Komposte aus Abfällen (Kompost Verordnung 2001) (Austrian ordinance on compost quality).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20001486
LGBl. Nr. 13/1994 zuletzt geändert durch LGBl. Nr. 45/2013 Gesetz über die Vermeidung und Behandlung von Abfällen und die Einhebung einer hierfür erforderlichen Abgabe im Gebiete des Landes Wien (Wiener Abfallwirtschaftsgesetz)(Viennese Waste Management Law).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=LrW&Gesetzesnummer=20000141
StF: BGBl. I Nr. 102/2002 zuletzt geändert durch BGBl. I Nr. 193/2013 Bundesgesetz über eine nachhaltige Abfallwirtschaft (Abfallwirtschaftsgesetz 2002 - AWG 2002) (Austrian Waste management law).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20002086
StF: BGBl. II Nr. 570/2003 zuletzt geändert durch BGBl. II Nr. 498/2008 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft über ein Abfallverzeichnis (Abfallverzeichnisverordnung) (Waste catalogue ordinance).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20003077
StF: BGBl. I Nr. 141/2003, letzte Änderung BGBl. I Nr. 23/2013 Tiermaterialiengesetz 2013 Bundesgesetz betreffend Hygienevorschriften für nicht für den menschlichen Verzehr bestimmte tierische Nebenprodukte und Materialien (Tiermaterialiengesetz - TMG) (Law on animal substances).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20003102
StF: BGBl. II Nr. 316/2010 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft, mit der Bestimmungen zur Durchführung des Futtermittel-gesetzes 1999 erlassen werden (Futtermittelverordnung 2010) (Ordinance on animal feed 2010).
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20006949
StF: BGBl. II Nr. 484/2008, Änderung BGBl. II Nr. 141/2010 Verordnung der Bundesministerin für Gesundheit, Familie und Jugend über nähere Bestimmungen zum Umgang mit tierischen Nebenprodukten (Tiermaterialien-Verordnung) (Ordinance on animal substances).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20006148
StF: LGBl Nr 40/2010 Verordnung der Salzburger Landesregierung vom 10. Mai 2010 über die getrennte Erfassung biogener Abfälle (SalzburgerBioabfallverordnung 2010) (Salzburg Ordinance on biowaste 2010).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20006148
StF: BGBl. II Nr. 471/2011 Verordnung des Bundesministers für Wirtschaft, Familie und Jugend, mit der Preise für die Abnahme elektrischer Energie aus Ökostromanlagen auf Grund von Verträgen festgesetzt werden, zu deren Abschluss die Ökostromabwicklungsstelle im Jahr 2012 verpflichtet ist (Ökostromverordnung 2012) (Ordinance on green electricity).
Available from:
https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=20007631
D) VOLUNTARY AGREEMENT
The Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management, the Austrian Chamber of Commerce (WKÖ), the Austrian Chamber of Labour (AK), the Austrian Federation of trade unions (ÖGB) and the Austrian Chamber of Agriculture (LK)) (2013) Action plan (in German).
Available from:
http://www.bmlfuw.gv.at/land/lebensmittel/kostbare_lebensmittel/partner.html
E) RESEARCH AND TECHNICAL REPORTS
Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management, (2012), Sekundärstudie Lebensmittelabfälle in Österreich (Food waste in Austria).
No weblink available.
Lebersorger, S., Schneider, F. (2014), Food loss rates at the food retail, influencing factors and reasons as a basis for waste prevention measures. Waste Management, 34 (11), 1911–1919.
Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.06.013
Schneider, F (2013), The evolution of food donation with respect to waste prevention. Waste Management, 33 (3), 755–763.
Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.10.025
Lebersorger S., Schneider F. (2011), Discussion on the methodology for determining food waste in household waste composition studies. Waste Management, 31 (9-10), 1924-1933.
Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21705207
Salhofer S., Obersteiner G., Schneider F., Lebersorger S. (2008), Potentials for the prevention of municipal solid waste. Waste Management, 28 (2), 245-259.
Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17442562
F) COMMUNICATION AND CAMPAIGNS
Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (BMLFUW), Lebensmittel sind kostbar (Food is precious) (in German).
Available from: http://www.bmlfuw.gv.at/land/lebensmittel/kostbare_lebensmittel/schule.html
Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (BMLFUW), Viktualia award (in German).
Available from: http://www.bmlfuw.gv.at/land/lebensmittel/kostbare_lebensmittel/viktualia/viktualia.html
Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management (BMLFUW), Die besten Restl-Rezepte (The best recipes with waste), (in German).
Available from: http://www.bmlfuw.gv.at/land/lebensmittel/kostbare_lebensmittel/restl-rezepte.html
Austrian food-sharing online platform (in German).
Available from: http://at.myfoodsharing.org/
Ideenwettbewerb „Lebensmittel sind Kostbar“ (Competition of ideas “food is precious”), (in German).
No web link available.
Lebensmittel sind kostbar (Food is precious- City of Salzburg), (in German).
Available from: http://www.stadt-salzburg.at/pdf/kostbare_lebensmittel_2012.pdf
Lebensmittel sind kostbar (Food is precious- Tyrol), (in German).
Available from: http://www.atm-online.at/index.php?page=lebensmittel-sind-kostbar
Lebensmittel sind kostbar (Food is precious- Upper Austria), (in German).
No web link available.
Series of lectures “Sustainability in Vienna” (Nachhaltig in Wien), (in German).
No web link available.
Symposium “Food is valuable” (Lebensmittel sind wertvoll!), (in German).
No weblink available.
Neighbourhood project towards surplus food transfer (Vienna).
No weblink available.
Wasted Food (Lower Austria), (in German).
Available from: http://www.noe.gv.at/Umwelt/Abfall/Ressourcenschonung/Lebensmittel_im_Abfall.html
Action platform “Food waste in Styria”, (in German).
Available from: http://www.nachhaltigkeit.steiermark.at/cms/ziel/96223473/DE
Initiative „Restl Festl – Graz isst auf“ (Surplus event – Graz eats all up), (in German).
Available from: http://restlfestl.wordpress.com
G) PROJECTS AND OTHER MEASURES
Environmental Education in Schools- ÖKOLOG (in German).
Available from: http://www.oekolog.at/das-ist-oekolog.html
Ecobusiness plan - The Environmental Service Package of the City of Vienna (in German).
Available from: https://www.wien.gv.at/english/environment/protection/eco/index.html
All links cited in the references have been accessed for the last time on October 27, 2015.

 Copyright © 2016 | EU FUSIONS |
Copyright © 2016 | EU FUSIONS |